The larvae feed mainly on roots but they will also eat corms and soft fleshy stems. It takes several months to develop from egg to adult resulting in one cycle per year on outdoor crops but multiple generations may occur on heated crops.
Find out more about our vine weevil controls
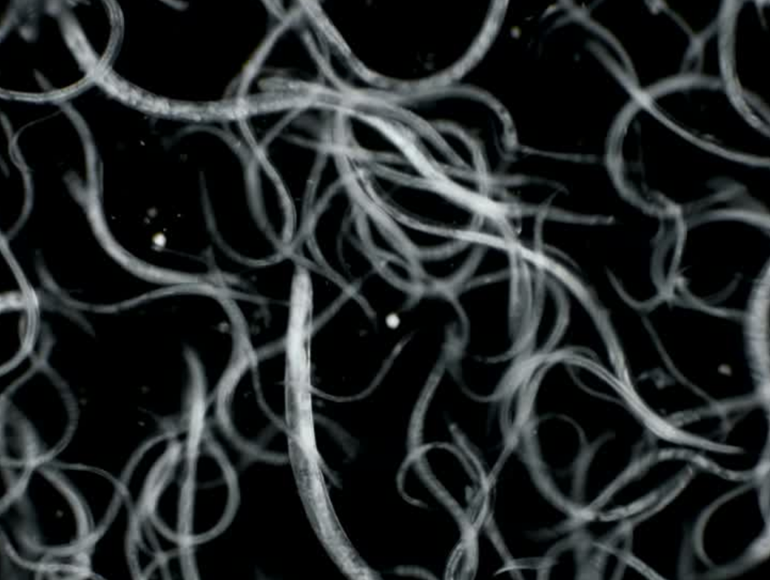
Steinernema kraussei - Microscopic nematode worms seek out vine weevil larvae in the soil and compost, larger weevil grubs are more easily located. Nematodes enter the weevil larvae and release a small pellet of bacteria that kills the host after a few days.
The parasitic worms begin to reproduce, releasing several thousand more juvenile infective nematodes able to find and kill further weevil grubs.
Heterorhabditis bacteriophora - Microscopic nematode worms seek out vine weevil and chafer grub in the soil and compost, larger weevil grubs are more easily located. Nematodes enter the weevil larvae and release a small pellet of bacteria that kills the host after a few days. The parasitic worms begin to reproduce, releasing several thousand more juvenile infective nematodes able to find and kill further weevil grubs.
Autumn and spring are the main seasons for nematode application, although additional treatments may be needed for heated or protected crops. It is important that the soil or compost or turf is kept moist (not water logged).
Steinernema carpocapsae - The traps consist of a specially designed wooden board. It's 3 grooves are filled with a gel containing 2.5 million nematodes (Steinernema carpocapsae), which swell when in contact with water, forming a raft.
Adult beetles crawl into the grooves, looking for shelter, and are attacked by the nematodes.
Each trap is effective for approximately 6 weeks.